Data Lens
Evaluation of the impact of WHO outlier tool training to data managers and M&E officers at District and Health Centre level in Rwanda on data quality.
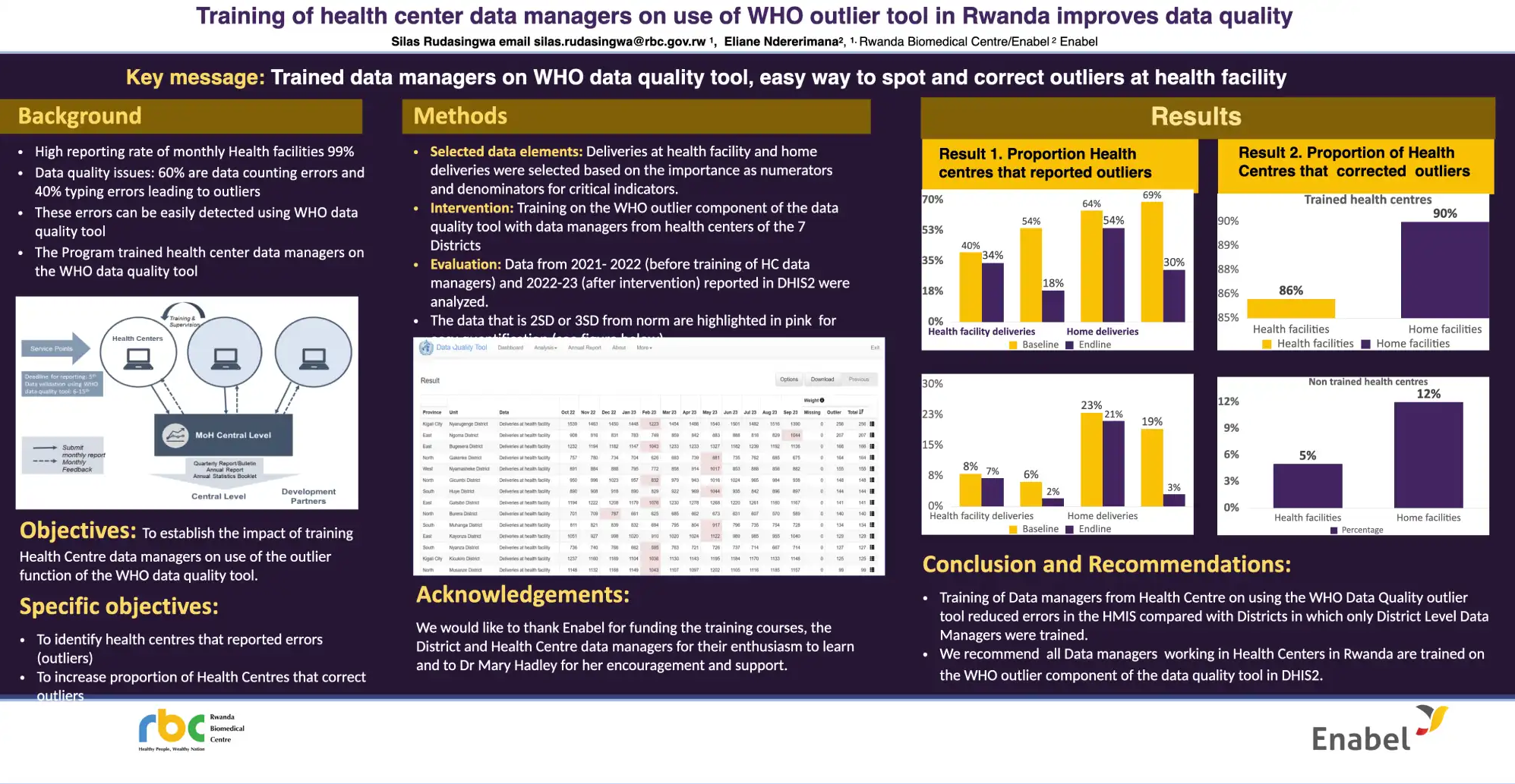
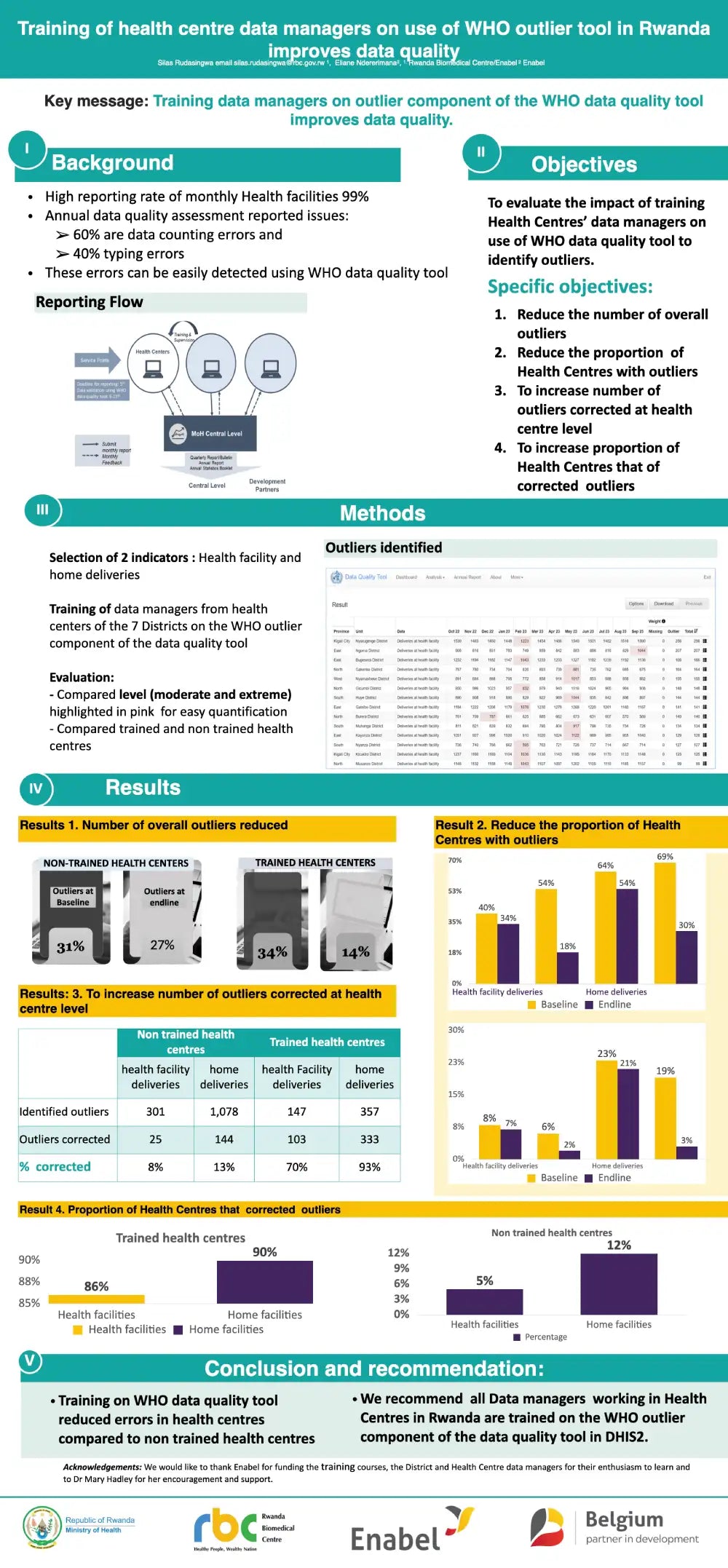
Accuracy of data in the routine Health Management Information System is critical to allow evidenced-based prioritised use of scarce resources and to determine effective interventions. In Rwanda, annual data quality assessments found that 60% data errors are counting errors and 40% data errors are typing errors. Both these errors can be easily identified during desk review by data managers. The WHO data quality tool is included in the DHIS2 portal in Rwanda.
Training on the use of the tool to District level Data Managers and M&E officers was widespread. However, funding to train all data managers at health centre level was not forthcoming but one, Belgian funded project trained all health centres in seven Districts. An evaluation showed that the number of outliers decreased from 31% to 27 % compared with 34% to 14% in the health centres where training was provided. Furthermore, while only 13% outliers were corrected in health centres without training, 93% were corrected in those where training was provided.
We concluded that data quality can be improved through use of the WHO data quality tool but that training to health centre level will further reduce typing and counting errors. Let us know your experiences on reducing data errors in the DHIS2 portal.